A computer network (or data network) is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data. The physical connection between networked computing devices is established using either cable media or wireless media. The best-known computer network is the Internet.
HISTORY
Before the advent of computer networks, communication between calculation machines and early computers was performed by human users by carrying instructions between them. Today, in spite of the wide use of email and other networking applications, people do continue to transfer information to another person's computer by hand-carrying removable storage media (such as flash drives) — a method jokingly known as "sneakernet".
In September 1940, George Stibitz used a teletype to send instructions for a problem set from his Model at Dartmouth College to hisComplex Number Calculator in New York and received results back by the same means.
In the late 1950s, early networks of communicating computers included the military radar system Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE).
In 1960, the commercial airline reservation system semi-automatic business research environment (SABRE) went online with two connected mainframes.
In 1962, J.C.R. Licklider developed a working group he called the "Intergalactic Computer Network", a precursor to the ARPANET, at the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA).
In 1964, researchers at Dartmouth developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System for distributed users of large computer systems. The same year, at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, a research group supported by General Electric and Bell Labs used a computer to route and manage telephone connections.
Throughout the 1960s, Leonard Kleinrock, Paul Baran and Donald Davies independently conceptualized and developed network systems which used packets to transfer information between computers over a network.
In 1965, Thomas Marill and Lawrence G. Roberts created the first wide area network (WAN). This was an immediate precursor to the ARPANET, of which Roberts became program manager.
Also in 1965, the first widely used telephone switch that implemented true computer control was introduced by Western Electric.
In 1969, the University of California at Los Angeles, the Stanford Research Institute, the University of California at Santa Barbara, and the University of Utah were connected as the beginning of the ARPANET network using 50 kbit/s circuits.[2]
In 1972, commercial services using X.25 were deployed, and later used as an underlying infrastructure for expanding TCP/IPnetworks.
In 1973, Robert Metcalfe wrote a formal memo at Xeroc PARC describing Ethernet, a networking system that was based on theAloha network, developed in the 1960s by Norman Abramson and colleagues at the University of Hawaii. In July 1976, Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs published their paper "Ethernet: Distributed Packet Switching for Local Computer Networks" and collaborated on several patents received in 1977 and 1978. In 1979, Robert Metcalfe pursued making Ethernet an open standard.
In 1976, John Murphy of Datapoint Corporation created ARCNET, a token-passing network first used to share storage devices.
In 1995, the transmission speed capacity for Ethernet was increased from 10 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. By 1998, Ethernet supported transmission speeds of a Gigabit. The ability of Ethernet to scale easily (such as quickly adapting to support new fiber optic cable speeds) is a contributing factor to its continued use today.[4]
Today, computer networks are the core of modern communication. All modern aspects of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) are computer-controlled. Telephony increasingly runs over the Internet Protocol, although not necessarily the public Internet. The scope of communication has increased significantly in the past decade. This boom in communications would not have been possible without the progressively advancing computer network. Computer networks, and the technologies that make communication between networked computers possible, continue to drive computer hardware, software, and peripherals industries. The expansion of related industries is mirrored by growth in the numbers and types of people using networks, from the researcher to the home user.
Type of network
Local area network (LAN)
- is a small computer network that usually using in short connection.
- Connection in same or near area.
- Connection from 2 computers and tools or more.
- If want far connection, must use repeater together.
Metropolitan area network
- is a large computer network or aggregation of LAN.
- Cover wide areas in citys.
- must use Backbone which serves as a connection main line.
Wide area network
- is a computer network that covers a large geographic area.
- uses a communications channel that combines many types of media such as telephone lines, cables, and air waves.
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
Network topology is the layout or organizational hierarchy of interconnected nodes of a computer network.
A bus network: all nodes are connected to a common medium along this medium. This was the layout used in the original Ethernet, called 10BASE5and 10BASE2.
A star network: all nodes are connected to a special central node. This is the typical layout found in a Wireless LAN, where each wireless client connects to the central Wireless access point.
A ring network: each node is connected to its left and right neighbour node, such that all nodes are connected and that each node can reach each other node by traversing nodes left- or rightwards. The Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) made use of such a topology.
A mesh network: each node is connected to an arbitrary number of neighbours in such a way that there is at least one traversal from any node to any other.
A fully connected network: each node is connected to every other node in the network.
วันจันทร์ที่ 16 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2556
Home Network
HOME NETWORK
Creating a home network.
For houses with many members. And use almost all computers. We are able to build up a home network. Then connect all the computers together. To be able to exchange information between each other and access the Internet just an single county.Network technology in the home.Because the home is the wiring. Telephone line out already. It can be something that is available to make the network. Eliminating the need for new cabling. Home network technologies can be divided into the following five together.• Ethernet network technology, a Bus.• The Ethernet Technology Network Star.• phone line networking technology.• powerline networking technology.• The wireless network technology.Networking technology for Ethernet Bus.Network technology, Ethernet and Bus Mult 10Base2 using the Coaxial (cattle Pontiac special) called Thin Coaxial cable or RG-58 (with a resistance of 50 ohms), the overall length of the line from the origin to the destination machine. must not exceed 180 meters, but the model is low cost because it does not require a hub in the middle - a signal.Ethernet network technology, a Star.Network technology, Ethernet and Star as standard 10BaseT is a form of wired UTP (Unshield Twisted Pair), which is a small line within eight strands twisted together four pairs in the - in the Speed 10/100 Mbps with a signal. Base band and the length of each cable line from the hub must not exceed 100 feet (80 meters should be a good way to avoid interference).Connection is suitable for home use because it can be easy to move the machine and disconnect the Island. As for the cost, since it is very inexpensive 8-port hubs are around 1,000 baht.Telephone network technologies.Telephone network or telephone lines went Phoneline Network is bringing them home. The connection between computers.Usually it will be phone wiring in every room in the house. We just put a network adapter. Used for connecting to a phone line to plug into. The computer can use it.Know HomePNA.Organization that looks after the network using standard phone lines will be called HomePNA trusted name www.homepna.org. A source of information about the products used to connect network phone lines in Figure 5.5 transfer speeds - Send information about 10 megabits per second T (10 Mbps) as the technology to be used for qualified Inernet Gateway as the other systems.Network cables.Network wiring (Powerline Network) or Power Line Communication. Is bringing the power lines went inside to get laid - send data.(User must have a device converts the data from the signal generator) power line networking technology can be - in both the large data files. Including high speed internet surfing 5.4 megabits per second. (On the modem speed is about 56 kilobytes per second), the basic operation of electric network. When the signal is high frequency information from the Internet, which he would send a signal to the local power station. To supply electricity to every home. Users will need a special adapter for plugging into an outlet at home. Then converted - Field signal in both picture and sound from the electrical signals. Then send them to the computer or other electrical unit used to.Organizations controlled using standard network cables is HomePlug Powerline A lliance by combining the different device manufacturers leading networks such as AMD, CISCO, Compaq, Intel, Motorola, 3COM, etc. have a site name.www.homeplug.org.The Company's technology is designed Intellon chip (Chip) for embedded computers. And other electrical components of Figure 5.8 to see how technology Intellon Homeplug 1.0 Compliant with speeds up to 14 megabits per second.Wireless network technology.Wireless network (Wireless) has developed a range of more than five years for the greater good. Do not want to clutter the wiring Portland meeting room VIP customers park or area. Land can not be hardwired.But we take the computer to the user in a broadcast radius. It has a radius ranging from 80 to 400 feet of wireless network technology are two different types.First.HomeRF (Home Radio Frequency).Two. IEEE 802.11.HomeRF (Home Radio Frequency) is the product of the Group Cayman System, Compaq Ciemens, Intel, Motorola, and Proxim, designed for use at home. Allows us to carry a notebook to work in any room in the home. Or to sit the E-mail and the Internet to find information on home turf it. Land lines are no longer interested in the silk cloth? Because HomeRF systems use frequency 2.4 GHz (Ka Chi Hz) for penetrating walls wall obstacles. In the - information. This system has a radius of about 150 feet with speed - Transfer files to 10 megabits per second by the HomeRF 2.0.IEEE 802.11b was designed and developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE or the I triple E) network is known as IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN (WLAN) uses radio frequency 2.4 GHz (. shift registers Hz) for - information. This system will have a radius of about 80 to 300 feet from the access point. Or it may be up to 100 meters high - in file 11 megabits per second. Network Wireless Wireless LAN is composed of two parts: the Access Point (access points) and PC cards by the second part is to receive - signal frequency 2.4 GHz agencies have tested and approved these products. the WECA (Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance) has a website www.wi-fi.com. For in wallpaper form. There are two companies involved in the chip design of the two companies.Security. Receiving - IEEE 802.11b wireless data transmission, there are likely to be intercepted. Capture data as well. So before you get products WiFi security checks. Which is the standard WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a data encryption (Data Encryption) and 40 to 64-bit and 128-bit encryption to secure the data.Wireless LAN Speed 5 GHz.IEEE 802.11b wireless networking is gaining speed - 5 to 11 megabits per second data transmission and data encryption. There are many manufacturers of the United States and European countries began to develop design standards IEEE 802.11a, which uses radio frequencies 5 GHz (Ka Chi Hz), the material can transmit data at a speed of 22 to 72 MHz. bits per second and supports Quality of Service for multimedia applications such as video with sound.Because the manufacturer states to use 802.11b standard, which is similar to the Ethernet system is Listen before Transmitting or listen before, but use European standard HIPERLAN / 2 in the time slot will be similar to the ATM. difference between the two standards will cause problems for users of the equipment is not available for use in the U.S., Europe and the United States. I can not take it.Equipment in use in Europe as well.
Computer hardware
วันจันทร์ที่ 2 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2556
Computer hardware
Computer hardware
 |
| PDP-11 CPU board |
Google Modular Data Center
Google Modular Data Center
The Google Modular Data Center is a set of shipping containers used by Google to house its servers. They were revealed on April 1, 2009, during the first Google Data Center Efficiency Summit in Mountain View, California. The data centers are rumored to cost $600 million USD each, and use from 50 to 103 megawatts of electricity. They house the computing resources that comprise the Google platform.
History
Link
Link Blog
- Keetapat Pawongchit
- Jakkrapan Chamjaidee
- Jirapak Thaphatom
- Chayabhorn Gamonsakpitak
- Chatchanan Wiwatpassawon
- Yanapat Limrachadawong
- Tarasut Peachawat
- Pichitchai Kamonkon
- Wongsapat Srimaksook
- Worawich Thepkaew
- Watcharapong Limtagunthongchai
- Witchakorn Munlajit
- Sarayut Rugbandon
- Sitthipon Merit
- Akarawin Atthanak
- Nut Tangphoom
- Trerat Insawang
- Tiwisiri Buaban
- Tanrada Bunreangrod
- Premruthai sriboonpeng
- Warissara Wattana
- Sasiprapa Nakpan
- Siwaporn Duangkaew
- Suchittra Inboon
- Atikan Jampagin
- Arissara Jitdamrongkanti
- Unchisa Nakthong
วันพุธที่ 4 กันยายน พ.ศ. 2556
Google X
As you know, Google - is not only a search engine: The company is a world leader in the creation of gadgets, internet services, and more. The most curious development team is engaged in a secret Google X, and among their projects - here are 10 ideas that the Internet giant seeks to bring to life.
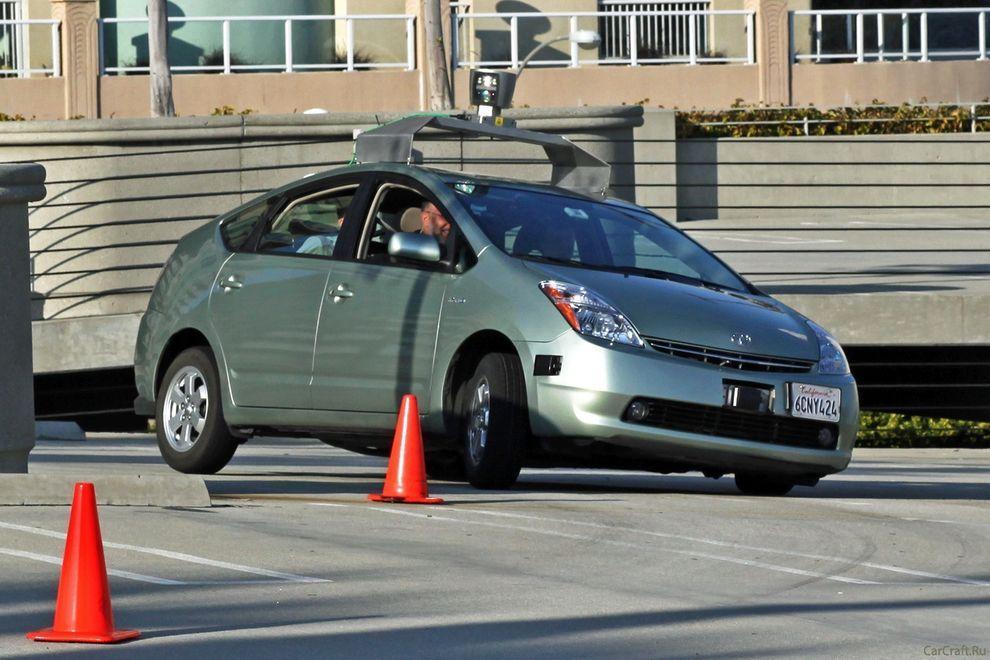

1. Car without a driver will make road traffic safer
Experts of Google X for several years working on the project Driverless Car Program. Negotiations are underway with the authorities for permission to test the self-governing vehicles on public roads - as long as this agreement only states of California and Nevada. A fleet of ten vehicles with test systems allow run over more than 480 thousand km (as of August of 2012), and of course, tests are continuing. However, it is unclear when such a system will be commercially available.
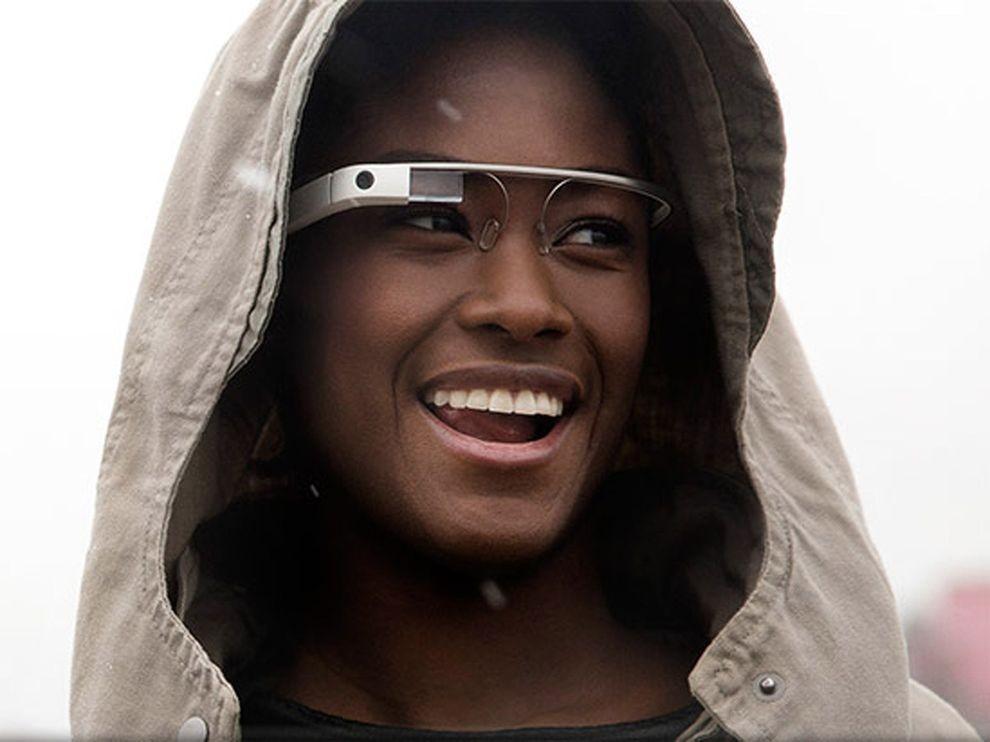

2. Google Glass will change the way you think about gadgets
Having put on those glasses, you can forget about the screens of smartphones and computers - the right information will always be available in only one eye movements. One way to look up - and before you calendar, email, social networks, weather, in general, everything that you want. Google Glass makes a revolutionary technology available to a wide range of people so far only a few lucky people, mostly developers and journalists were able to get a working prototype of points, but the consumers opportunity arises next year
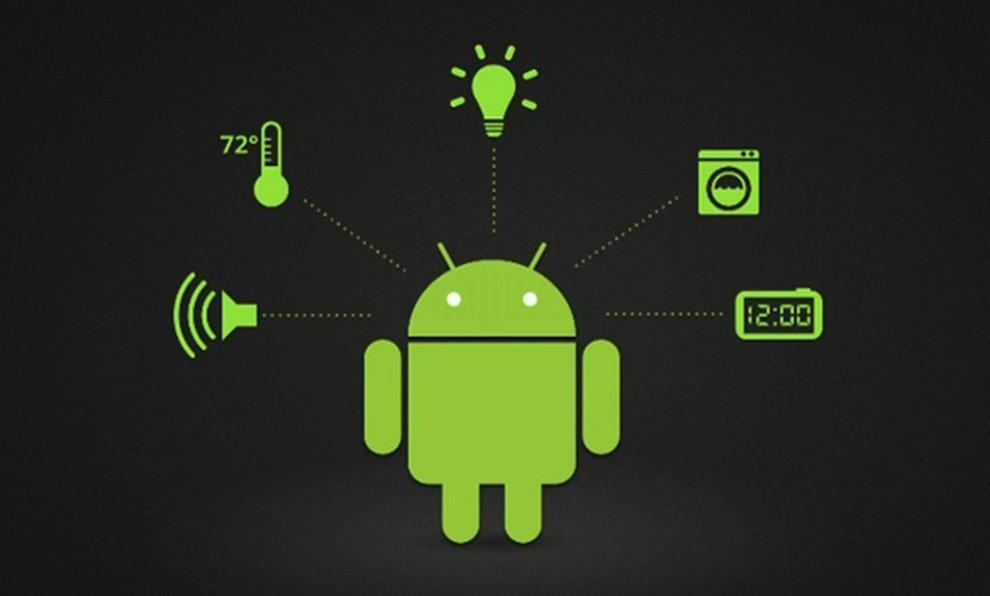
3. "Smart House" according to Google
The technology, called Android @ Home, will fully automate all of the life support system by connecting to the Internet, for example, while you are not home, a refrigerator will be able to order the necessary products itself, and coffee maker to make coffee exactly to your arrival. Android @ Home will connect all electrical appliances.
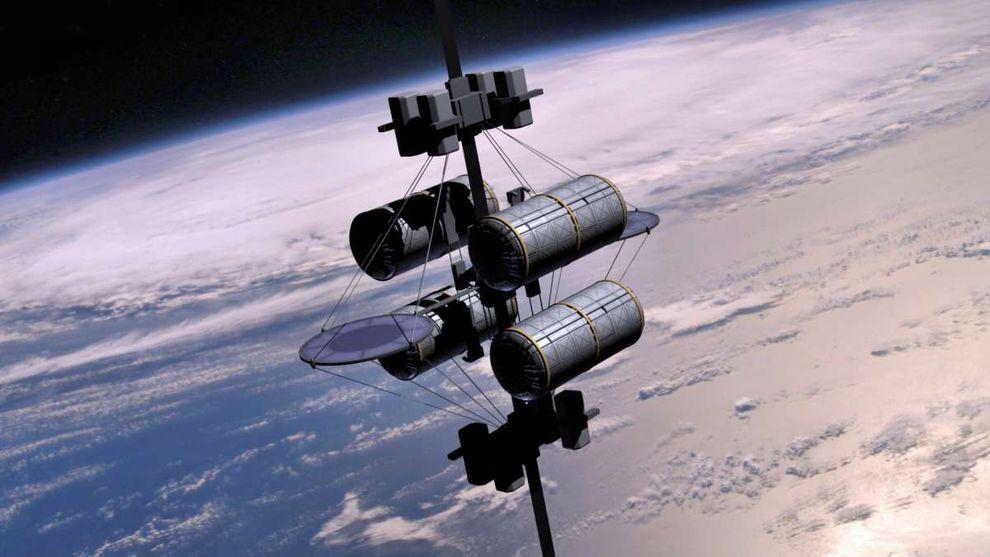

4. Space elevator
According to published in the journal «Time» information Google X team in 2011, the year included the idea of a "space elevator" in the so-called list of "What if ...". I must say, the very concept of this method of delivery to the orbit of people and goods put forward by K. Tsiolkovsky in 1895, the year. Do not wait for Google's early implementation of this idea - the development of "lift into orbit," presents many technical challenges, and all the more likely to say that to implement this idea in life is impossible. However, it's probably Google thus "cover their tracks" to save the process of developing a secret.

5. Watch a smartphone based on Android
Recently, it was reported that Google is preparing a direct competitor iWatch from Apple - a watch, combined with the smartphone: of course, watches SmartWatch smartphone from Google will use the operating system Android. This latest «must have»-new to the gadget lovers will be available early next year.






1. Car without a driver will make road traffic safer
Experts of Google X for several years working on the project Driverless Car Program. Negotiations are underway with the authorities for permission to test the self-governing vehicles on public roads - as long as this agreement only states of California and Nevada. A fleet of ten vehicles with test systems allow run over more than 480 thousand km (as of August of 2012), and of course, tests are continuing. However, it is unclear when such a system will be commercially available.

2. Google Glass will change the way you think about gadgets
Having put on those glasses, you can forget about the screens of smartphones and computers - the right information will always be available in only one eye movements. One way to look up - and before you calendar, email, social networks, weather, in general, everything that you want. Google Glass makes a revolutionary technology available to a wide range of people so far only a few lucky people, mostly developers and journalists were able to get a working prototype of points, but the consumers opportunity arises next year

3. "Smart House" according to Google
The technology, called Android @ Home, will fully automate all of the life support system by connecting to the Internet, for example, while you are not home, a refrigerator will be able to order the necessary products itself, and coffee maker to make coffee exactly to your arrival. Android @ Home will connect all electrical appliances.

4. Space elevator
According to published in the journal «Time» information Google X team in 2011, the year included the idea of a "space elevator" in the so-called list of "What if ...". I must say, the very concept of this method of delivery to the orbit of people and goods put forward by K. Tsiolkovsky in 1895, the year. Do not wait for Google's early implementation of this idea - the development of "lift into orbit," presents many technical challenges, and all the more likely to say that to implement this idea in life is impossible. However, it's probably Google thus "cover their tracks" to save the process of developing a secret.

5. Watch a smartphone based on Android
Recently, it was reported that Google is preparing a direct competitor iWatch from Apple - a watch, combined with the smartphone: of course, watches SmartWatch smartphone from Google will use the operating system Android. This latest «must have»-new to the gadget lovers will be available early next year.

6. Google will take care of your health
The Internet giant has a stake in the company Adimab, engaged in the development of diagnostics and treatment of various diseases, which would bring a variety of technologies and methods to combat diseases. The revolutionary idea is the invention of miniature sensors involved in the search and optimization of antibodies produced by the body - to start treatment only need to swallow such a sensor. Another development in the field of Google Health is a subsidiary of iPierian, creating the technology of "cellular reprogramming» (cellular reprogramming), which will fight the disease by modifying cells.
The Internet giant has a stake in the company Adimab, engaged in the development of diagnostics and treatment of various diseases, which would bring a variety of technologies and methods to combat diseases. The revolutionary idea is the invention of miniature sensors involved in the search and optimization of antibodies produced by the body - to start treatment only need to swallow such a sensor. Another development in the field of Google Health is a subsidiary of iPierian, creating the technology of "cellular reprogramming» (cellular reprogramming), which will fight the disease by modifying cells.

7. Internet airships cover the entire planet wireless
Google's ambitions as a provider of Internet reached all-time highs - the company is developing airships that will provide wireless connectivity the entire planet, including remote regions in Africa and other parts of the Earth. If the project is realized, the "world wide web" will get about another 1 billion people - mostly residents of the "third world."

8. Game console based on Android
The popularity of the Android platform is growing all over the world, and Google is seeking to use its potential to the maximum.
«Wall Street Journal» spoke about the development of the gaming console from Google, which is designed to be a "killer" similar technology "Yabloko» - Apple TV: game console from Google allows you to run any Android-games directly on your home television.

9. The way Google determines the development of smart phones Motorola
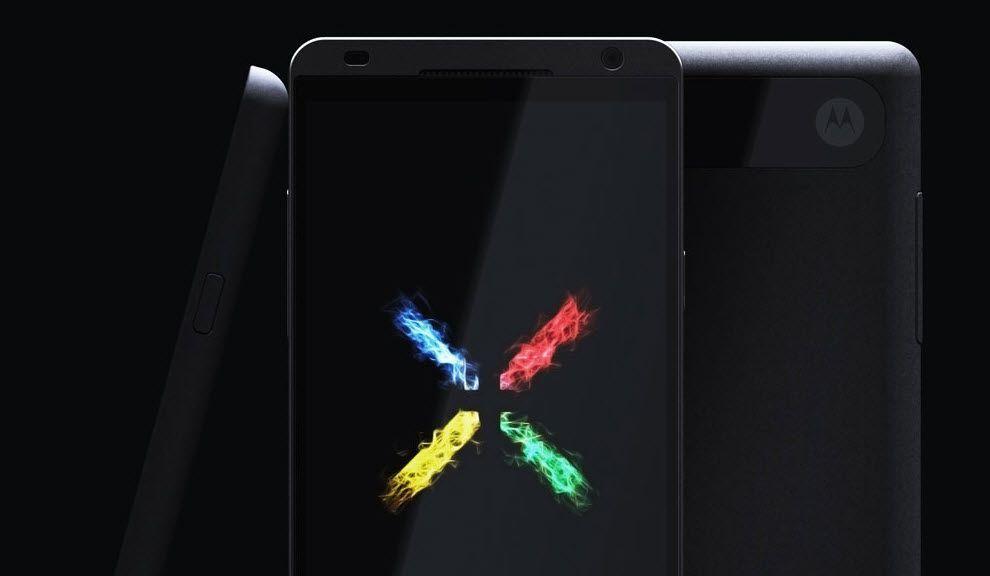
Buy Google of Motorola Mobility (transaction was $ 12.5 billion) to become the owner of the first allowed 24.5 thousand patents and designs. Under the wing of the Internet giant will release a smartphone Motorola Moto X based on Android, which has all the modern features and characteristics, as well as, of course, a number of trendy "chips", which has no rivals - release date already quite close.

10. Eco-friendly sources of energy
The company Makani Power - developer of advanced technologies in the use of wind and solar energy: Google previously invested in the company a lot of money, and recently acquired in its entirety and included in the project, which deals with Google X. The best-known development Makani Power - wind turbines, hovering at an altitude of almost 300 m to 650 m-minute and allow to generate electricity out of thin
How to Build a Water Cooled PC
If you are new to liquid cooling, or if you've never purchased Koolance products in particular, you may be wondering what is required to get started. A typical water cooling system consists of four main parts (see also: Liquid Cooling 101):
A Radiator (heat exchanger) with fans to move heat from liquid into air
Water Blocks to transfer heat into liquid
A Pump to move the liquid
A Reservoir for automatically filtering air from the liquid and storing excess coolant
There are many practical water cooling configurations depending on your application and preferences. You should begin your decision based on which components will be water cooled. Regardless of whether you're cooling a computer or something else, the expected heat output and desired temperature range of these areas will dictate many of your liquid cooling parts.
Determining Approximate Heat Output
Hardware is designed with a TDP, or "Thermal Design Power" in mind. This is the maximum amount of heat a cooling system is expected to handle for that component at normal clock speed and voltage. Here is a rough guide:
CPU Processor: 60-150W
Video Card
Single GPU (low-end): 100W
Single GPU (mid-range): 150-250W
Single GPU (high-end): 200-350W
Dual GPU (high-end): 300-450W
Motherboard
Chipset: 10-30W
Voltage Regulators: 5-20W
Memory: 2-5W per stick
Hard Drive (regular or SSD): 10-30W
The two primary targets for water cooling in a PC computer are the CPU and video graphics card. These areas produce the highest amount of heat and benefit most from liquid cooling. We can consider these "high heat" sources (a dual-GPU video card should be considered as two high heat sources). The remaining areas on the motherboard, RAM, and hard drives are considered "low heat" sources. Low heat components can be considered in aggregate, but they don't usually contribute enough heat to significantly affect radiator selection.
.
Choosing a Radiator

Heat exchanger size and airflow are critical to a PC water cooling system's performance-- moreso than liquid flow rate. For this reason, it's recommended to use the largest radiator you can comfortably fit into your workspace, computer chassis, etc. Larger radiators are advantageous because they decrease liquid temperature and can allow for quieter fan speeds.
What is the minimum radiator size needed if you have space constraints? Our suggested minimum sizes are based on the number of "high heat" devices (CPU or GPU) you will liquid cool:
1 device = 1 fan radiator
2 devices = 2 fan radiator
3 devices = 3 fan radiator
4 devices = 4 fan radiator
5+ devices = larger than 4 fans, or use multiple radiators
These are only recommendations. The "correct" option is based on your desired temperature and noise range. Some customers find it acceptable to cool 4 video cards with a 3-fan radiator by accepting a somewhat higher temperature range, and/or by running the fans faster. Downsizing too much is something to avoid, though, since it's entirely possible to choose a radiator which is too small to handle a heat load.
Koolance lists "FPI" (fins per inch) for its heat exchangers, which is the fin density. This can be relevant for users deciding to do one of the following:
Emphasize cooling performance and opt for the largest, highest fin density radiator allowable. Pair it with high CFM/pressure fans. Generally, 120mm fans push more air than 140mm fans.
Emphasize lower noise levels by selecting a lower fin density radiator. Use medium-range fans and/or voltage-throttle them. Generally, 140mm fans are quieter than 120mm fans.
Low fin density radiators will still improve with more airflow, and high fin density radiators can be quieted by reducing fan speed, so there is a lot of room for tweaking. Either decision should result in significantly lower chip temperatures than air cooling (see recommended radiator sizes above).
Selecting Water Blocks

Koolance has a range of individual water blocks broken down by category. For PC cooling, a convenient Product Selection Tool is also offered. After supplying some basic hardware criteria, this page will generate a list of potential water blocks to use in your future cooling system. Also see our water block help pages under "Information->Product Help" above. If you require assistance, please let us know.
Finding a Pump

Koolance offers several pumps of various specifications. The more cooling components added to a cooling loop, the stronger the pump needed to counter flow restriction. For a typical computer cooling loop with a 3-fan radiator and a few water blocks, any pump offered by Koolance should provide enough flow.
Flow rate tends to be over-emphasized in PC cooling. For the majority of loops, effective flow rates higher than 1.5-2.0 LPM (0.4-0.5 GPM) won't contribute much, if anything, to thermal performance. A reliable pump is important, as is making sure it's strong enough to keep adequate flow through your selected components. But for users looking to improve thermal performance, increasing radiator size and airflow is almost always more effective.
Keep in mind that the maximum flow rate listed for pumps is at zero static head pressure, while the maximum static head is at zero flow rate. That means the actual flow rate in a cooling system will usually be quite a bit lower than the pump's maximum specification.
The Reservoir

The primary purpose of a reservoir is to bleed air from the loop and to store extra liquid to reduce maintenance. It won't assist with cooling aside from delaying the time required to reach maximum heat saturation. Reservoirs are also a good opportunity to show off your water cooling system. The size and type of reservoir is based solely on aesthetics and available space. A large, LED-lit reservoir with UV colored coolant mounted against a side window or front drive bay will be highly visible. Hose Size and Fittings (6mm, 10mm, or 13mm?) Tubing is based on allowable space and personal preference. 6mm (1/4in) internal diameter hose is a good option for compact areas like servers and media centers. For computers with more space, 10mm (3/8in) or 13mm (1/2in) ID is recommended. There are few situations where 13mm (1/2in) ID hose outperforms 10mm (3/8in) in temperature, so we encourage this choice based primarily on whichever looks best to you.
Your fittings will follow the hose size you choose. Be sure that both the ID (internal diameter) and OD (outer diameter) of your fittings match your selected hose size. Hose barbs, unlike compression fittings, will accept different outer diameters by changing the clamp (the ID must still match). Barbs require pliers to install the clamp, while compression fittings are secured by hand.

Water cooling for GPU only.

This one too.
A Radiator (heat exchanger) with fans to move heat from liquid into air
Water Blocks to transfer heat into liquid
A Pump to move the liquid
A Reservoir for automatically filtering air from the liquid and storing excess coolant
There are many practical water cooling configurations depending on your application and preferences. You should begin your decision based on which components will be water cooled. Regardless of whether you're cooling a computer or something else, the expected heat output and desired temperature range of these areas will dictate many of your liquid cooling parts.
Determining Approximate Heat Output
Hardware is designed with a TDP, or "Thermal Design Power" in mind. This is the maximum amount of heat a cooling system is expected to handle for that component at normal clock speed and voltage. Here is a rough guide:
CPU Processor: 60-150W
Video Card
Single GPU (low-end): 100W
Single GPU (mid-range): 150-250W
Single GPU (high-end): 200-350W
Dual GPU (high-end): 300-450W
Motherboard
Chipset: 10-30W
Voltage Regulators: 5-20W
Memory: 2-5W per stick
Hard Drive (regular or SSD): 10-30W
The two primary targets for water cooling in a PC computer are the CPU and video graphics card. These areas produce the highest amount of heat and benefit most from liquid cooling. We can consider these "high heat" sources (a dual-GPU video card should be considered as two high heat sources). The remaining areas on the motherboard, RAM, and hard drives are considered "low heat" sources. Low heat components can be considered in aggregate, but they don't usually contribute enough heat to significantly affect radiator selection.
.
Choosing a Radiator

Heat exchanger size and airflow are critical to a PC water cooling system's performance-- moreso than liquid flow rate. For this reason, it's recommended to use the largest radiator you can comfortably fit into your workspace, computer chassis, etc. Larger radiators are advantageous because they decrease liquid temperature and can allow for quieter fan speeds.
What is the minimum radiator size needed if you have space constraints? Our suggested minimum sizes are based on the number of "high heat" devices (CPU or GPU) you will liquid cool:
1 device = 1 fan radiator
2 devices = 2 fan radiator
3 devices = 3 fan radiator
4 devices = 4 fan radiator
5+ devices = larger than 4 fans, or use multiple radiators
These are only recommendations. The "correct" option is based on your desired temperature and noise range. Some customers find it acceptable to cool 4 video cards with a 3-fan radiator by accepting a somewhat higher temperature range, and/or by running the fans faster. Downsizing too much is something to avoid, though, since it's entirely possible to choose a radiator which is too small to handle a heat load.
Koolance lists "FPI" (fins per inch) for its heat exchangers, which is the fin density. This can be relevant for users deciding to do one of the following:
Emphasize cooling performance and opt for the largest, highest fin density radiator allowable. Pair it with high CFM/pressure fans. Generally, 120mm fans push more air than 140mm fans.
Emphasize lower noise levels by selecting a lower fin density radiator. Use medium-range fans and/or voltage-throttle them. Generally, 140mm fans are quieter than 120mm fans.
Low fin density radiators will still improve with more airflow, and high fin density radiators can be quieted by reducing fan speed, so there is a lot of room for tweaking. Either decision should result in significantly lower chip temperatures than air cooling (see recommended radiator sizes above).
Selecting Water Blocks

Koolance has a range of individual water blocks broken down by category. For PC cooling, a convenient Product Selection Tool is also offered. After supplying some basic hardware criteria, this page will generate a list of potential water blocks to use in your future cooling system. Also see our water block help pages under "Information->Product Help" above. If you require assistance, please let us know.
Finding a Pump

Koolance offers several pumps of various specifications. The more cooling components added to a cooling loop, the stronger the pump needed to counter flow restriction. For a typical computer cooling loop with a 3-fan radiator and a few water blocks, any pump offered by Koolance should provide enough flow.
Flow rate tends to be over-emphasized in PC cooling. For the majority of loops, effective flow rates higher than 1.5-2.0 LPM (0.4-0.5 GPM) won't contribute much, if anything, to thermal performance. A reliable pump is important, as is making sure it's strong enough to keep adequate flow through your selected components. But for users looking to improve thermal performance, increasing radiator size and airflow is almost always more effective.
Keep in mind that the maximum flow rate listed for pumps is at zero static head pressure, while the maximum static head is at zero flow rate. That means the actual flow rate in a cooling system will usually be quite a bit lower than the pump's maximum specification.
The Reservoir

The primary purpose of a reservoir is to bleed air from the loop and to store extra liquid to reduce maintenance. It won't assist with cooling aside from delaying the time required to reach maximum heat saturation. Reservoirs are also a good opportunity to show off your water cooling system. The size and type of reservoir is based solely on aesthetics and available space. A large, LED-lit reservoir with UV colored coolant mounted against a side window or front drive bay will be highly visible. Hose Size and Fittings (6mm, 10mm, or 13mm?) Tubing is based on allowable space and personal preference. 6mm (1/4in) internal diameter hose is a good option for compact areas like servers and media centers. For computers with more space, 10mm (3/8in) or 13mm (1/2in) ID is recommended. There are few situations where 13mm (1/2in) ID hose outperforms 10mm (3/8in) in temperature, so we encourage this choice based primarily on whichever looks best to you.
Your fittings will follow the hose size you choose. Be sure that both the ID (internal diameter) and OD (outer diameter) of your fittings match your selected hose size. Hose barbs, unlike compression fittings, will accept different outer diameters by changing the clamp (the ID must still match). Barbs require pliers to install the clamp, while compression fittings are secured by hand.

Water cooling for GPU only.

This one too.
Codemasters
Codemasters Software Company Limited, or Codemasters (earlier known as Code Masters) is a British video game developer and publisher founded by David Darling and his brother Richard in 1986. Codemasters is one of the oldest surviving British game studios, and in 2005 was named the top independent games developer byDevelop magazine. But now Codemasters change their name to "Codemasters Racing" because they don't want to try a lot of money to made RPG, FPS games, and don't complete. They say "We will stop made RPG or FPS game, Codemasters will go ahead to the racing games"
Codemasters founded in 1986 by Richard and David Darling (who worked previously for Mastertronic), Codemasters established themselves in the growing ZX Spectrum market, mostly with action games that required the player to solve simple puzzles by combining different objects, such as the Dizzy series. While rooted in the ZX Spectrum, Codemasters did not write exclusively for this computer - they also released software (including the Dizzy series) for the Commodore 64, Commodore 16,BBC Micro, Acorn Electron, Amstrad CPC, Atari 8-bit, Commodore Amiga and Atari ST.
They were famous for releasing a long series of "Simulator" games, mostly sports simulations (such as Pro Boxing Simulator). This led to the parody "Advanced Lawnmower Simulator" being developed, praised to the skies and then published byYour Sinclair magazine as an April Fool's Day stunt.
Computer program
"Computer program code" and "Software code" redirect here. For their source form, see source code. For the machine-executable code, see machine code.
A computer program, or just a program, is a sequence of instructions, written to perform a specified task with a computer.[1] A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor.[2] The program has anexecutable form that the computer can use directly to execute the instructions. The same program in its human-readable source codeform, from which executable programs are derived (e.g., compiled), enables a programmer to study and develop its algorithms. A collection of computer programs and related data is referred to as the software.
Computer source code is typically written by computer programmers. Source code is written in a programming language that usually follows one of two main paradigms: imperative or declarative programming. Source code may be converted into an executable file(sometimes called an executable program or a binary) by a compiler and later executed by a central processing unit. Alternatively, computer programs may be executed with the aid of an interpreter, or may be embedded directly into hardware.
Computer programs may be ranked along functional lines: system software and application software. Two or more computer programs may run simultaneously on one computer from the perspective of the user, this process being known as multitasking.
สมัครสมาชิก:
ความคิดเห็น (Atom)




